Bitrix24. Changing the encoding of the Bitrix24 website from CP-1251 to UTF-8, notes
Andy Wits Blog

We'll use official documentation: training.bitrix24.com/support/training...
I would like to add a few additional points on my own.
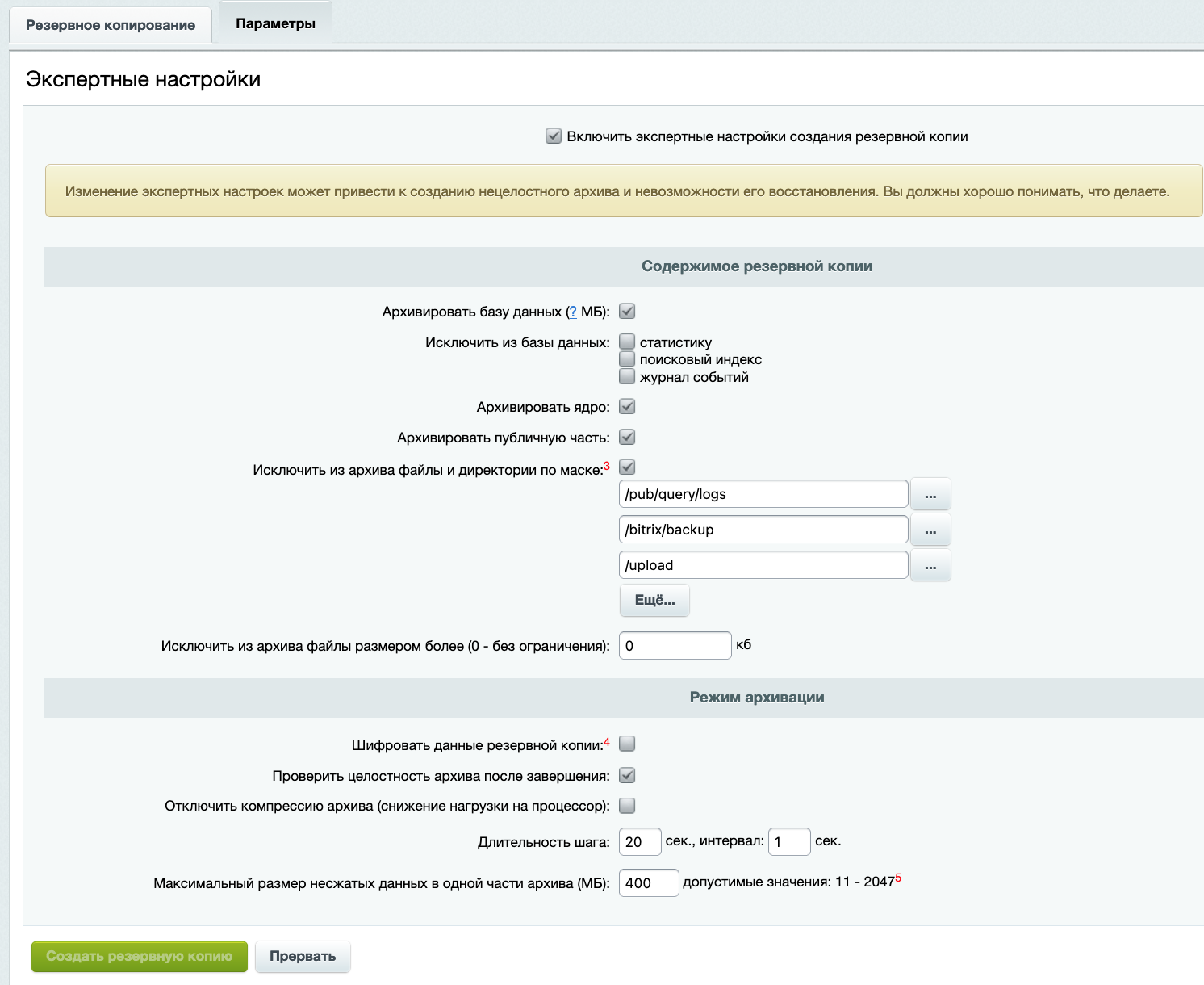
Before step 1, we will make the necessary backups. We will make sure that there is no one on the site and do it manually with expert settings, but without backups and storage, to save space. We have backups with storage in regular backups, right? :)
tar --exclude="upload" --exclude="bitrix/backup" -czvf bitrix.YOURNAME.com.tar.gz bitrix.YOURNAME.com
Also, before recoding files, it would be good to have a separate backup of files. Let's go to the /home/bitrix folder and do:
cd /home/bitrix
tar --exclude="upload" --exclude="bitrix/backup" -czvf bitrix.YOURNAME.com.tar.gz www
where "www" are the files of the Bitrix site.
But these are not all the configuration files where the encoding can be written. It turned out that we also have local value written, as indicated on the phpinfo page:
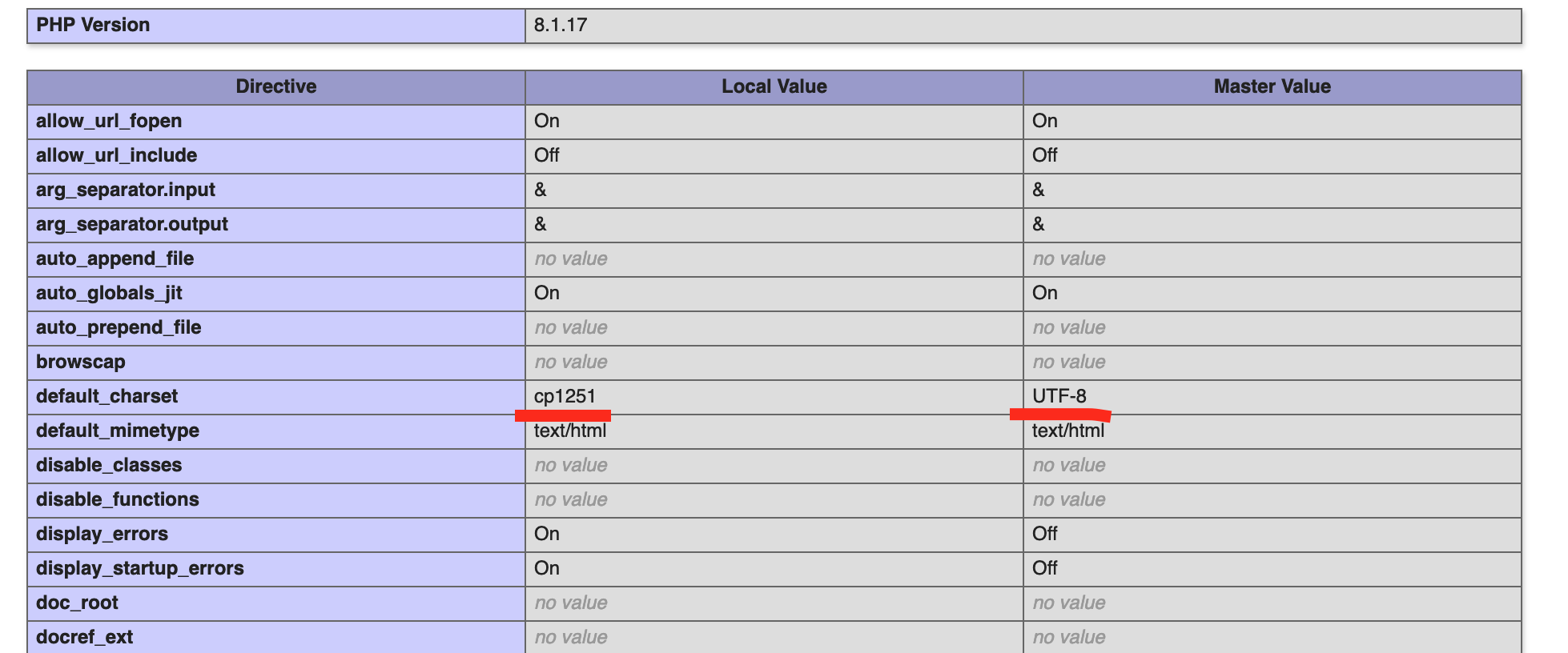
I found that in these files:
/etc/httpd/bx/conf/bx_ext_bitrix.YOURNAME.com.conf
/etc/httpd/bx/conf/default.conf
the parameter was registered:
php_admin_value default_charset cp1251
I had to comment out this line and politely ask Apache to reread the config:
apachectl graceful
(see the link to the manual at the beginning)
To convert the database, we get a list of queries, as indicated in the manual. For convenience, the generated list of queries can be saved to a file and placed in the folder from where we launched mysql -u ... in the terminal on the server
and then execute the queries from the file:
source bitrix_new_utf8_convert.sql;
For example, in the file "bitrix/php_interface/after_connect_d7.php" you need to change the code to this:
<?
$this->queryExecute("SET NAMES 'utf8'");
$this->queryExecute('SET collation_connection = "utf8_unicode_ci"');
?>
The script that is offered in the manual is not the most optimal. We will improve it. I found that in addition to the Russian language in the cp1251 encoding, there are other languages, but they were added later and all of them are in utf-8. Also, the English language in the default encoding iso...
Here is a command that will find all files, excluding those that are utf-8, display them on the screen one by one and convert them, leaving a copy of each file, adding ".icv" to it:
find ./ -name "*.php" -type f |
while read file
do
if ! file -bi $file | grep -q 'utf-8'
then
echo " $file"
mv "$file" "$file".icv
iconv -f WINDOWS-1251 -t UTF-8 "$file".icv > "$file"
fi
done
There will be quite a few .icv files, tens of thousands. They can be counted with the command:
cd /home/birix/www
find ./ -name "*.php.icv" -type f | wc
Later, if everything is OK, these copies can be deleted with the following command:
cd /home/birix/www
find ./ -type f -name '*.php.icv' -delete
If you still use xargs, it's better to do it like this:
cd /home/birix/www
find ./ -type f -name '*.php.icv' -print0 | xargs -0 rm
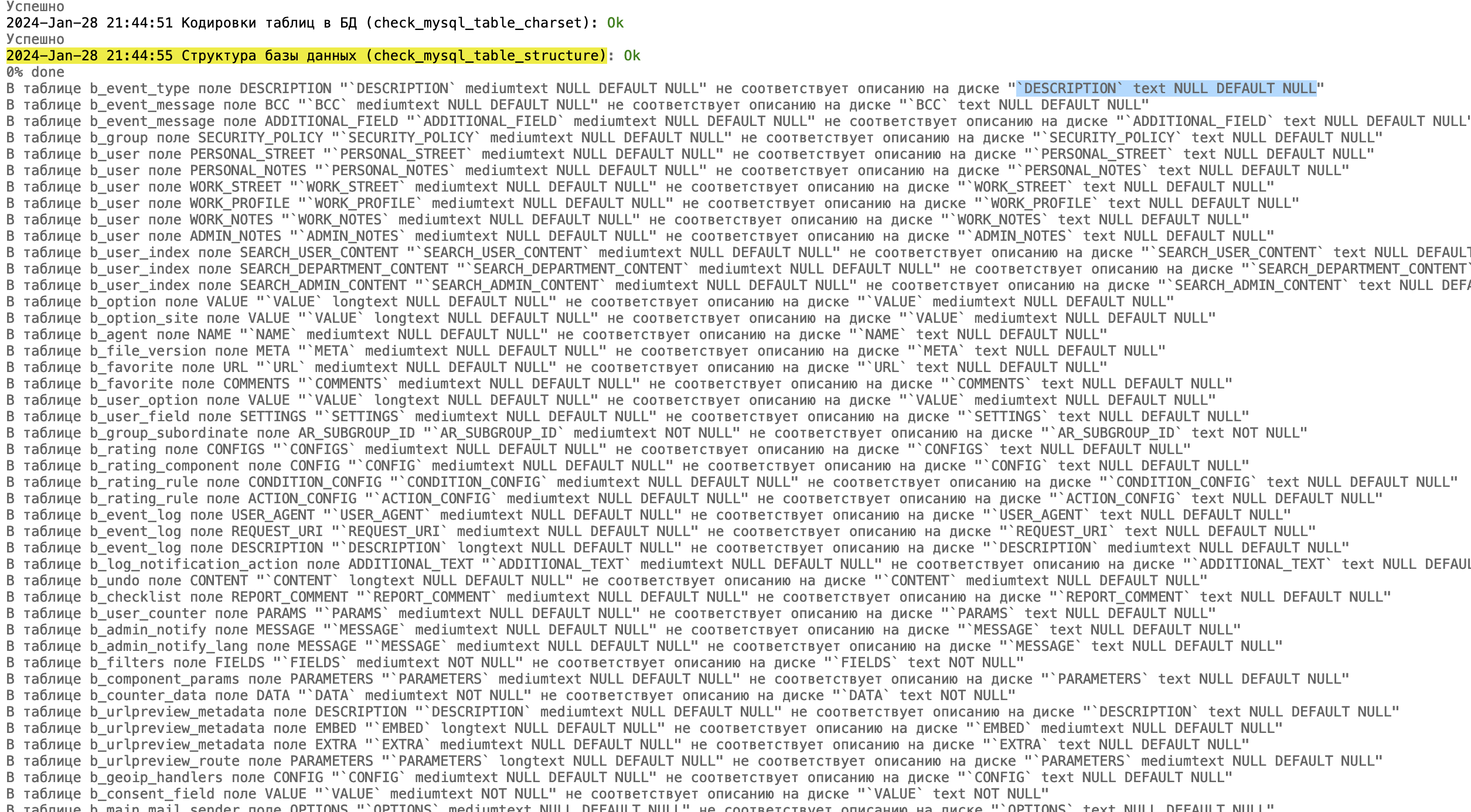
To fix them, you can simply run the suggested queries via the console.
However, 2 queries did not work for me:
ALTER TABLE `bitrix_88`.`b_search_stem` CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
ALTER TABLE `bitrix_88`.`b_search_tags` CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
I found that it may be necessary to manually correct some tables in the DB, since they have "COLLATE cp1251_bin":
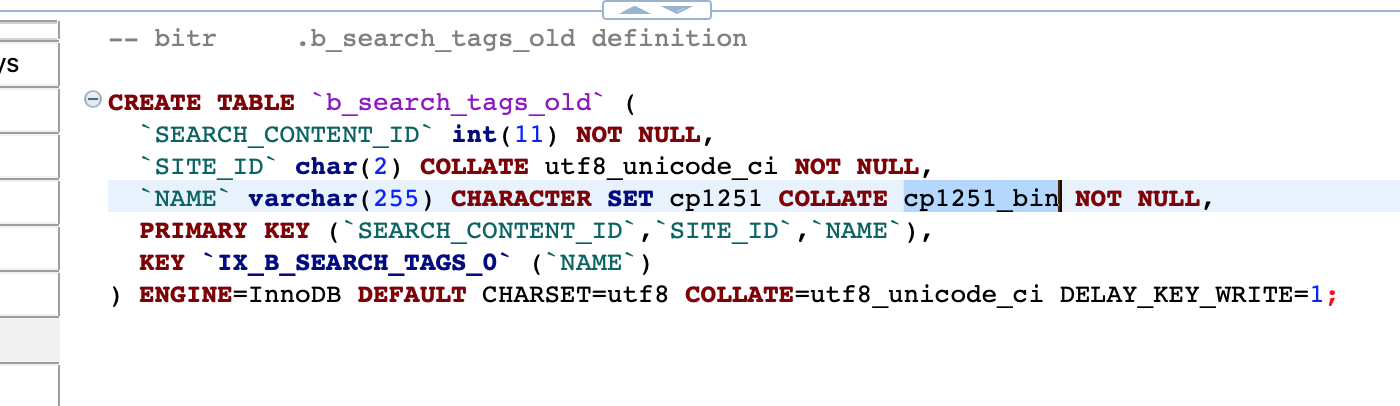
I found this solution: recreate such tables. That is, make clean copies, recode and delete the old ones:
CREATE TABLE b_search_stem_new LIKE b_search_stem;
ALTER TABLE b_search_stem_new CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
INSERT INTO b_search_stem_new SELECT * FROM b_search_stem ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE STEM = VALUES(STEM);
ALTER TABLE b_search_stem RENAME b_search_stem_old;
ALTER TABLE b_search_stem_new RENAME b_search_stem;
// then you can delete the *_old table:
DROP TABLE b_search_stem_old;
CREATE TABLE b_search_tags_new LIKE b_search_tags;
ALTER TABLE b_search_tags_new CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
INSERT INTO b_search_tags_new SELECT * FROM b_search_tags ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE NAME = VALUES(NAME);
ALTER TABLE b_search_tags RENAME b_search_tags_old;
ALTER TABLE b_search_tags_new RENAME b_search_tags;
// then you can delete the *_old table:
DROP TABLE b_search_tags_old;
(Data that is not really needed in them. But if you want, you can make a dump).